The Needs Theory: Motivating Employees with Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
After you watch the video and know the material, click HERE for the quiz.
Hunger, thirst, security, friendship, respect and being all that you can be are just some of the things that motivate us to take action. This lesson helps us to further understand these needs and how they motivate behavior by showing where they fall in Maslow's hierarchy of needs.
Needs Theory of Motivation
Effectively motivating employees has long been one of management's most important and challenging duties. Motivation refers to the psychological processes that stimulate excitement and persistence of voluntary actions aimed at some goal. Because motivation can be highly individualized, managers use a wide range of techniques to keep their employees motivated and happy. Therefore, it is essential for managers to understand the psychological processes involved in motivation so that they can effectively direct employees towards organizational goals.
 |
Needs theories attempt to identify internal factors that motivate an individual's behavior and are based on the premise that people are motivated by unfulfilled needs. For example, if you were dissatisfied with living in your parents' basement at age 40, you might go out and find your own apartment. In doing so, you will fulfill the need for privacy, independence and the ability to bring a date home without having to explain why you still live with your parents. Needs are psychological or physiological insufficiencies that provoke some type of behavioral response. The needs a person has can range from weak to strong and can vary based on environmental factors, time and place.
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs Theory
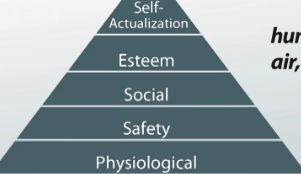
One of the most popular needs theories is Abraham Maslow's hierarchy of needs theory. Maslow proposed that motivation is the result of a person's attempt at fulfilling five basic needs: physiological, safety, social, esteem and self-actualization. According to Maslow, these needs can create internal pressures that can influence a person's behavior.
 |
Physiological needs are those needs required for human survival such as air, food, water, shelter, clothing and sleep. As a manager, you can account for physiological needs of your employees by providing comfortable working conditions, reasonable work hours and the necessary breaks to use the bathroom and eat and/or drink.
Safety needs include those needs that provide a person with a sense of security and well-being. Personal security, financial security, good health and protection from accidents, harm and their adverse affects are all included in safety needs. As a manager, you can account for the safety needs of your employees by providing safe working conditions, secure compensation (such as a salary) and job security, which is especially important in a bad economy.
Social needs, also called love and belonging, refer to the need to feel a sense of belonging and acceptance. Social needs are important to humans so that they do not feel alone, isolated and depressed. Friendships, family and intimacy all work to fulfill social needs. As a manager, you can account for the social needs of your employees by making sure each of your employees know one another, encouraging cooperative teamwork, being an accessible and kind supervisor and promoting a good work-life balance.
Esteem needs refer to the need for self-esteem and respect, with self-respect being slightly more important than gaining respect and admiration from others. As a manager, you can account for the esteem needs of your employees by offering praise and recognition when the employee does well, and offering promotions and additional responsibility to reflect your belief that they are a valued employee.
 |
Self-actualization needs describe a person's need to reach his or her full potential. The need to become what one is capable of is something that is highly personal. While I might have the need to be a good parent, you might have the need to hold an executive-level position within your organization. Because this need is individualized, as a manager, you can account for this need by providing challenging work, inviting employees to participate in decision-making and giving them flexibility and autonomy in their jobs.
As the name of the theory indicates, Maslow believed that these needs exist in a hierarchical order. This progression principle suggests that lower-level needs must be met before higher-level needs. The deficit principle claims that a once a need is satisfied, it is no longer a motivator because an individual will take action only to satisfied unmet needs. If you look at this pyramid you can see how Maslow's needs are organized with basic physiological needs, such as air, food, water and sleep, at the bottom and the idea of self-actualization, or when a person reaches the full potential in life, at the top. Again, according to Maslow, before a person can take action to satisfy a need at any level on this pyramid the needs below it must already be satisfied. To better understand how Maslow's hierarchy works, let's take a look at the following example.
 |
Maslow's Needs in Context
Meet Eric. He is a young boy who just started his summer vacation and cannot wait to go outside and play with his friends. As he walks towards the door he hears his stomach growl and realizes that in his excitement he forgot to eat. Eric knows that he won't be able to have fun playing outside if he is hungry, so he stops off at the fridge and grabs a bite to eat, as well as a bottle of water to take with him outside in case he gets thirty. Eric has now satisfied his basic physiological needs.
Once outside Eric notices a creepy individual in a van sitting down the street who is offering his friends some bottled water to drink. Just then, Eric realizes he left his bottle of water sitting on the kitchen counter. Eric sure is thirsty, but this man makes Eric feel unsafe. Unfortunately, the need to satisfy his thirst is stronger than his need for safety, so Eric approaches the van and asks the man for some water to drink. When the man turns around, Eric sees that the man is none other than his fourth-grade teacher Mr. Jenkins. Eric's need for safety was fulfilled once he recognized that he was no longer in danger, but even if this need was not met, Eric still would have been able to fulfill the lower-level physiological need by getting water (even if the guy did not turn out to be someone Eric knew).
After playing outside for a few more hours with his friends, which satisfies Eric's social needs, a new kid on the block joins them. Eric's friend Mark introduces the new kid as Bruno. Bruno starts to bully Eric, which makes Eric feel unsafe. Even though Eric wants to continue to fulfill his social need by hanging out with his friends, he chooses to go back inside because his need for safety overrules his social needs. When Eric gets back inside, he reflects on how much self-respect he has and knows that he did not deserve to be treated like that by Bruno. He gets bored quickly and feels left out, so he heads back outside. Eric's social needs become more important than his esteem needs; while Eric knows Bruno will continue to insult him, he cares more about fulfilling his social needs by hanging out with the larger group.
 |
Eric really wants to be the most popular kid in his group; this is Eric's self-actualization need. He sees that goal getting closer when Bruno starts to pick on Mark, who currently holds the title of 'most popular'. Eric knows he could join Bruno and show that he is cooler than Mark and thus, more popular. However, Eric fears this may cause Mark to dislike him, and Eric's need for esteem and respect are more important to him than his need for self-actualization. So, he asks Bruno to stop teasing Mark. Eric knows there will be other chances to steal the title of 'most popular,' which won't tarnish his reputation as a nice guy.
Lesson Summary
Let's review. Needs theories attempt to identify internal factors that motivate an individual's behavior and are based on the premise that people are motivated by unfulfilled needs. One of the most popular needs theories is Abraham Maslow's hierarchy of needs theory. Maslow proposed that motivation is the result of a person's attempt at fulfilling five basic needs: physiological, safety, social, esteem and self-actualization.
- Physiological needs are those needs required for human survival such as air, food, water, shelter, clothing and sleep.
- Safety needs include those needs that provide a person with a sense of security and well-being. Personal security, financial security, good health and protection from accidents, harm and their adverse affects are all included in safety needs.
- Social needs, also called love and belonging, refer to the need to feel a sense of belonging and acceptance. Social needs are important to humans so that they do not feel alone, isolated and depressed. Friendships, family and intimacy all work to fulfill social needs.
- Esteem needs refer to the need for self-esteem and respect, with self-respect being slightly more important than gaining respect and admiration from others.
- Self-actualization needs describe a person's need to reach his or her full potential.
Maslow's theory is based on two principles. Progression principle suggests that lower-level needs must be met before higher-level needs. Deficit principle claims that a once a need is satisfied it is no longer a motivator because an individual will take action only to satisfied unmet needs.
As a manager, you should review the specific steps that can be taken to provide your employees with a means of satisfying all of Maslow's needs. Remember, a motivated employee is an asset to any organization and it is up to you to provide motivators to your employees.