What Are the Different Parts of a Graph?
After you watch the video and know the material, click HERE for the quiz.
Being able to read a graph isn't just vital for an algebra class. Graphs and charts are used everywhere! We'll take a crash course on the basic x/y plane used in algebra and give you the fundamental vocab you need.
This lesson is on the different parts of a graph. Knowing the vocabulary for the different parts of the graph is really useful because it allows you to do more than just draw it on your paper and think about it in your head; it allows you to talk about it with other people and express what you're doing in words.
Graphs in the Real World
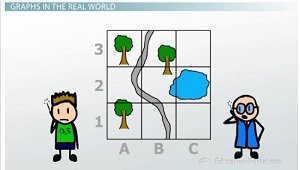 |
Graphs and grids are used outside of math to help people talk about lots of different things. For example, maps; when two people are looking at a map - maybe they're on radios talking about the same map, not even in the same spot - they can say where they're looking by using quadrants and grids on the map to say that, 'Oh, I'm looking at the lake that's near the quadrant C2.'
People can play chess that are in totally different places by saying things like, 'I move my Queen from A1 to A3.' That vocabulary allows them to express exactly what they're meaning without having to draw a picture that's physically there.
The Cartesian Plane
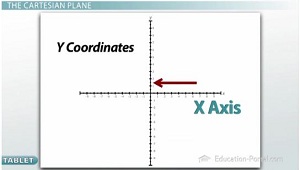 |
The graph that is most often used in algebra is what's called the Cartesian plane. The coordinates that go from left to right are the x-coordinates, which means that the line going left to right through the middle of the graph is what is called the x-axis. The coordinates that go up and down are the y-coordinates, which makes the line though the middle going up and down the y-axis.
These two axes divide the plane up into four quadrants. The first quadrant is in the top right and they are labeled counter clockwise - Quadrant 2, Quadrant 3, Quadrant 4. Quadrant 1 is called Quadrant 1 because it's the place where both the x and the y are positive numbers, which means that as we go left on the x axis, we get the negatives, and as we go down on the y axis, we get the negatives.
Points on the Graph and Ordered Pairs
 |
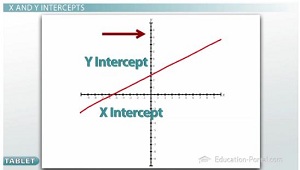
X and Y Intercepts
When we put a line on our graph, the place where that line crosses the two axes are special and they have special names. Because the left and right one is the x axis, the point where the line crosses the x-axis is called the x-intercept, and the point where the line crosses the y-axis is called the y-intercept.
 |
Lesson Summary
To review, our graph is called the Cartesian plane, or more simply, the x/y plane. We can label points with an x-coordinate and a y-coordinate, which when we put in parentheses give us an ordered pair.
 |
Anytime we draw a line on a graph, the point where that line crosses one of the axes is called an intercept.