How to Define a Zero and Negative Exponent
After you watch the video and know the material, click HERE for the quiz.
The zero and negative exponent properties are two you will use quite a lot in mathematics. The negative exponent property can be confusing, but when you remember a couple fun ideas, you will get it right every time!
Negative Exponent
In math, we like to write exponents with a positive number. So what happens if I get a negative exponent? What about a zero exponent?
 |
Before we get started, I need to tell you something important here: x^-a does not mean -x^a. The negative exponent has nothing to do with positive or negative numbers.
Let's look at the two formulas.
- x^-a = 1/(x^a)
- 1/(x^-a) = x^a
I want to make sure that you understand that x^-a does not mean -x^a. Once again, the negative exponent has nothing to do with positive or negative numbers. If the exponential is negative in the numerator, or the top, it tells us the exponential is actually positive in the denominator. If the exponential is negative in the denominator, or the bottom, it tells us the exponential is actually positive in the numerator.
 |
If you see a negative exponent, flip it to a positive. That is, if the exponent is negative in the numerator, flip it positive to the denominator. If the exponent is negative in the denominator, flip it positive to the numerator.
Let's say I have x^-4. Now remember, x^-4 can be written as a fraction (x^-4)/1. Remember, if it's negative in the numerator, you flip it positive to the denominator. So that's the same thing as saying 1/(x^4).
In this next example, x^-7 is in the denominator. We're going to flip it positive to the numerator. x^7 is the same thing as 1/(x^-7).
Zero Exponents
 |
I think the zero exponent is really fun! Basically, the formula says that anything - any number, any letter - raised to the zero exponent is always one. So when I have x^0, it's 1. Let's say I had something funny like 999,999^0. It's still 1!
The Quotient of Powers Rule says that when we divide exponentials with the same base, we subtract their exponents. So, I have (x^3)/(x^3). Remember, we subtract their exponents. So that would be x^(3-3), which is x^0.
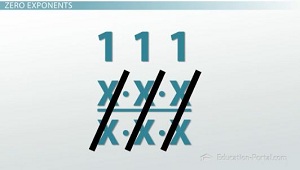 |
But where does the 1 come from? We have (x^3)/(x^3). That is, (x*x*x) on the top, or numerator, and (x*x*x) on the bottom, or denominator. x/x is 1, x/x is 1, and x/x is 1. When we multiply those together (1*1*1), we get 1! So that pretty much proves it: x^0 = 1!