Chapter 9
Security Market Efficiency and Returns
By Boundless
Types of stock market transactions include IPO, secondary market offerings, secondary markets, private placement, and stock repurchase.

There are three main types of market organization that facilitate trading of securities: auction market, brokered market, and dealer market.
When accounting for capital gains and losses in the securities market, understanding reporting responsibilities and potential reductions is critical.
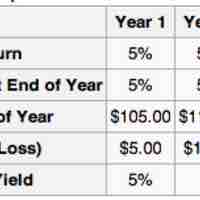
The dollar return is the difference between the final value and the initial value in nominal terms.
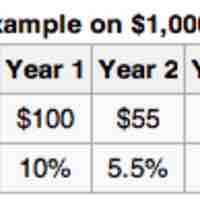
Percentage returns show how much the value of the investment has changed in proportion to the size of the initial investment.
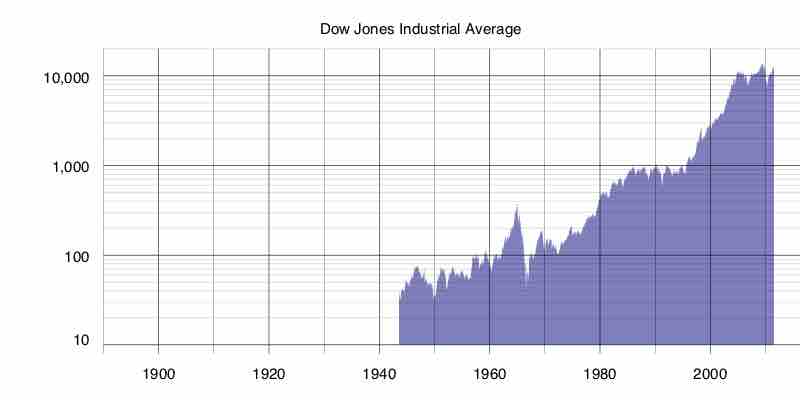
Markets and securities may follow general trends, but exogenous factors (such as macroeconomic changes) cause variability and volatility.
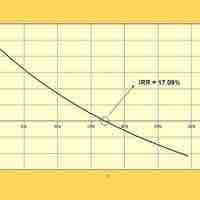
Average returns are commonly found using average ROI, CAGR, or IRR.
Efficient-market hypothesis (EMH) asserts that financial markets are informationally efficient and should therefore move unpredictably.
The EMH asserts that financial markets are informationally efficient with different implications in weak, semi-strong, and strong form.
The limitations of EMH include overconfidence, overreaction, representative bias, and information bias.

The Securities Act of 1933 ensures investors receive complete and accurate information before they invest.

The Securities Exchange Act of 1934 is a law governing the secondary trading of securities, financial markets and their participants.

The 1975 amendments are to establish a national market system for the nationwide clearance and settlement of securities transactions.
The Sarbanes–Oxley Act is to set new or enhanced standards for all U.S. public company boards, management, and public accounting firms.
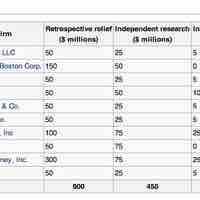
The Global Settlement was an enforcement agreement to address issues of conflict of interest within the SEC and other big investment companies.